|
 |
| |
| Waste to Energy |
|
The estimated that waste generation in India could be as much as 0.6 kilograms per person per day. India has only one-third the land space required when it comes to finding suitable locations for final disposal.India’s rapid population growth only magnifies the problem. The urban population has grown at a rate of more than 20 percent each year since 1980 and is projected to reach a rate of more than 30 percent by 2015. The poorly organized waste management scheme will continue to result in serious health problems and irreversible damage to the environment.
Worldwide, the dominant methods of waste disposal are to place the waste materials into landfills or on open rubbish tips. Although this disposal method has low initial costs, it presents a number of serious side effects:
- Air and water pollution leading to diseases
- Produce obnoxious odours
- Landfills release methane, which is an explosive gas with a high global warming potential
- Suitable sites for land filling are becoming scarce.
- High cost of disposal
What is M-WTE?
Waste-to-energy (WtE) or energy-from-waste (EfW) in its strictest sense refers to any waste treatment that creates energy in the form of electricity or heat from a waste source that would have been disposed of in landfill.
The term „Waste-to-Energy‟ means the use of modern combustion technologies to recover energy, usually in the form of electricity and steam, from mixed municipal solid wastes. These new technologies can reduce the volume of the original waste by 90%, depending upon composition and use of outputs
Converting disposal problems to prosperity
The landfills poses more problems than any other mode of waste disposal. Emissions from landfills are arguably the biggest landfill environmental problems. They result in depletion of air, water and land and the effects are as follows
- Noise, dust, odour, and possibly bio-aerosols, predominantly from landfill site operation;
- Landfill gas - from soon after opening and for possibly several hundred years thereafter.
- Comprise the potential emission of leachate and contaminated surface water run-off to, watercourses (ditches, streams, rivers etc) thus creating health hazards
- Pollution of groundwater in permeable strata below the landfill.
- Results in health hazards spreading commutable and infectious diseases
The waste is worth a whole lot of energy. The amount of energy generated depends on the quality of waste generated. The WTE is also applied for industrial wastes and literally any kind of waste that is disposed through landfills.
|
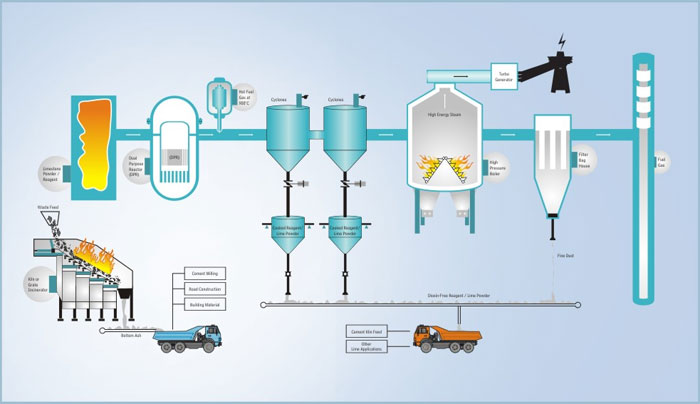
| WTE process diagram |
 |
| |
| Case Study |
The china case
Quanghzhou energy management system in Quanghzhou, China is a typical example of WTE model. Approximately 7000 tones of wastes were dumped in landfills from the year2005. Land filling is done in Chung shau all the year round and all wastes are processed here; they include incineration waste processing, volume reduction, harnessing and resource optimization. This process helps waste management and electricity production. About 80% of the 90% of volume of waste can be reduced after incineration process.
Warmer power generated by high heat fumes can be transformed into super heated steam,and it enters the turbine generator to generate power by 100%at the power sewage systems to heat the waste treatment process working with the firm load even when the turbine generator is at work. |
| |
|